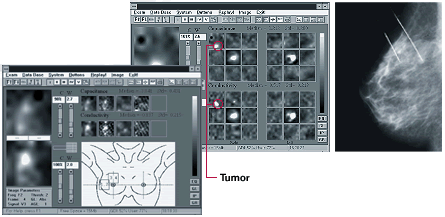
T-scan image screens left and middle, mammogram right
Images courtesy of TransScan Research and Development Co. Ltd.
Mammographic Findings:
The mammogram showed microcalcifications
(tiny calcium deposits that are an indicator of early breast cancer) and a 10 mm tumor
(mass) posteriorly in the upper, outer quadrant of the right breast (see the mammogram
image on the far right, the lower arrow points to the microcalcifications and the upper
arrow points to the mass).
T-Scan Findings:
Impedance imaging (center and left frame above) shows bright spots in the upper, outer
quadrant of the right breast, corresponding to the microcalcifications and the mass. The
white focal spot in the center of each display corresponds to the patient's nipple. The
only white object that should occur in T-scan examination of a normal breast is the
nipple. The targeted screen (with anatomic drawing) enables the physician to record
targeted views.
Histology (Laboratory
Testing of the Tissue Sample)
Lab testing of the tissue sample removed with biopsy (needle sampling) showed invasive
ductal carcinoma and ductal carcinoma in situ.
Note: "Ductal carcinoma" means the cancer developed from the linings of the breast ducts. "Invasive" means the cancer is marked by a tendency to spread, with cells that destroy the surrounding tissue. The term "in situ" is used to indicate an early stage of cancer in which a tumor is confined to the immediate area where it began. Specifically in breast cancer, in situ means that the cancer remains confined to ducts or lobules, and has not invaded the surrounding tissue in the breast nor spread to other organs in the body. In this particular case, both types of cells were obtained in the biopsy sample.
Updated: January 27, 2000



